The DT7816 provides a measure counter that you can use to measure the frequency, period, or pulse width of a single signal or the time period between two signals and return the value in the analog input stream.
Using software, you must define a signal to start the measurement operation and a signal to stop the measurement operation. A variety of signals are supported. How you wire the signals depends on the signals that you want to use.
The following table lists the possible start and stop signals and the connections that are required for each signal type. Refer to the DT7816 User's Manual for more information on the features of the measure counter.
Possible Start and Stop Signals
Signal |
Connection Required |
A/D Conversion Complete |
No connection required. |
Tachometer input (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect to the Tachometer input. |
Digital input 0 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 0 (pin 1) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 0. |
Digital input 1 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 1 (pin 3) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 1. |
Digital input 2 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 2 (pin 5) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 2. |
Digital input 3 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 3 (pin 7) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 3. |
Digital input 4 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 4 (pin 9) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 4. |
Digital input 5 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/Dor D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 5 (pin 11) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 5. |
Digital input 6 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 6 (pin 13) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 6. |
Digital input 7 (falling edge or rising edge) |
Connect a digital input, external A/D or D/A trigger, external A/D or D/A clock input, C/T clock input, or C/T gate input to general-purpose input 7 (pin 15) of the Digital I/O header. By default, this is digital input 7. |
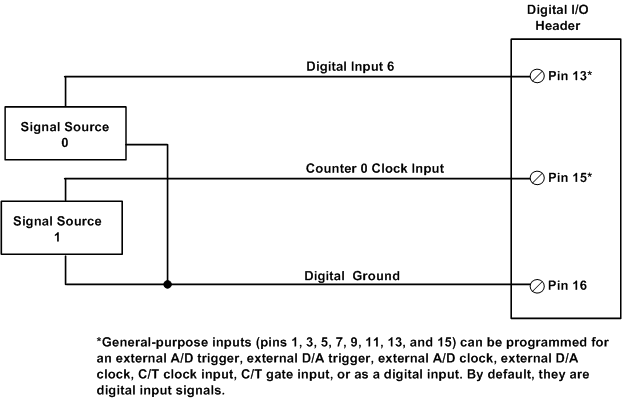
The following figure shows an example of connecting signals for a continuous edge-to-edge measurement operation using a measure counter. In this example, the signal that starts the measurement is the rising edge of the digital input signal connected to digital input 6 (pin 13). The signal that stops the measurement is the rising edge of the C/T input signal connected to general-purpose input 7 (pin 15). (You configure the signals/edges in software).
In this example, the measure counter is set up to measure the number of counts between the starting edge (the rising edge of the signal connected to digital input 6) and the stopping edge (the rising edge of the counter/timer input clock connected to pin 15). By including the measure counter in the analog input channel list, you can read the count and determine the time period between the two signals.

An Example of Connecting Signals for a Measure Counter Operation